Introduction
In the separate universe of Apple Inc., covered in mystery and protected by a culture suggestive of a furtive state, leaks have forever been viewed as the cardinal sin. From the period of Steve Occupations to the ongoing initiative of Tim Cook, the Cupertino-based tech monster has fastidiously created a climate where privacy is foremost. This article digs into the arresting story of apple insider trading by how insider data, or the deficiency in that department, assumes an essential part in forming the many-sided environment that is Apple. Analyzing the organization’s development, initiative changes, and key movements, we disentangle the layers of mystery that encompass Apple and investigate the fragile harmony between advancement, market predominance, and the steady fight against leaks .
An Inside Look At Apple’s Top-Secret Culture
Apple has fostered a culture that verges on paranoia when it comes to information breaches from its headquarters at 1 Infinite Loop, Cupertino. There is an ethos of strict secrecy around firm projects, innovations, and product launches until the time is right to release them to the public. According to many who have worked there before, secrecy is essential to the company culture and not merely a personal preference.
The Value Of Apple’s Security And Confidentiality Policies
Employees at Apple sign a plethora of non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) every year because the company places a premium on secrecy. Practices such as assigning codenames to projects and limiting attendance at meetings that lack adequate documentation highlight the necessity of protecting sensitive information. This isn’t just an internal issue; it shows that Apple is hell-bent on keeping its discoveries and strategies safe from rivals so it can keep up with the lightning-fast tech industry.
Tim Cook’s Priority In Maintaining Secrecy And Preventing Leaks
Since taking over as CEO in 2011, Tim Cook has reaffirmed Apple’s dedication to privacy. Cook has taken the initiative to resolve the matter of leaks within the company, recognizing the need of secrecy in maintaining Apple’s competitive advantage. Cook has shown his unfaltering commitment to maintaining the culture of secrecy that Jobs established by taking extreme measures to avoid information breaches, such as the 2017 presentation that warned staff against disclosing information.
Tim Cook’s Leadership And Changes

Tim Cook’s Succession To Steve Jobs
After Steve Jobs’s untimely death in 2011, Tim Cook became Apple’s chief executive officer. In contrast to Jobs’s more unconventional and visionary leadership style, Cook brought a more systematic and operational approach to the corporation. With the change in leadership, Cook became more concerned with improving Apple’s supply chain and operational efficiency.
Apple’s Success Under Tim Cook’s Guidance
During Cook’s tenure, Apple has grown at an unparalleled rate, surpassing all other tech companies in terms of market capitalization, which has surpassed $1 trillion. Cook’s mix of strategic business decisions, successful product releases such as the Apple Watch, and incremental improvements to the iPhone actively contributed to tracing back this expansion.
Moving Focus From Making Devices To Providing Services
With Cook at the helm, Apple has made a dramatic strategic shift, shifting its focus from product manufacturing to service provision. Projects such as Apple News+, Apple Pay, Apple Music, Apple TV+, and Apple Music+ all reflect this change. The hardware sales are just one source of revenue that the corporation hopes to broaden.
Growing The User Base And Assessing The Market
Cook’s leadership accounted for collecting over $1 trillion, comprising more than 66% of Mac’s market valuation, after Steve Jobs’ passing. The 1.4 billion dynamic clients are an immediate consequence of the gigantic development in the client base that has went with this monetary achievement. On account of its development, Apple is currently more present in individuals’ lives than any other time in recent memory.
Effects Of Apple On International Politics And Culture
Under Cook’s leadership, Apple has expanded its influence beyond technology and into culture and politics. With millions of customers around the world, the company’s goods and services have an impact on how people live their lives and what they value. Furthermore, its leadership, including Cook’s tight relationships with political personalities, positions Apple as a major actor in global politics.
The Superpower Status Of Apple
Metaphor Of Apple Park As A Secret Garden
Symbolic of Apple’s cloistered and secretive character is Apple Park. The park’s designation as a “secret garden” exemplifies the firm’s dedication to secrecy and control over information dissemination. The park’s regulated entry, well planned layout, and enclosed areas all contribute to its air of seclusion. Architects designed Apple’s offices to exude an air of secrecy, contributing to the exclusivity and mystery surrounding the company’s operations.
Evaluating The Cost Of Apple Park In Relation To The Nation’s Net Worth
Apple Park’s $5 billion price tag is a reflection of the company’s wealth and dedication to building a landmark headquarters. Drawing a comparison between this amount and the national net worth of nations—using Denmark as an example—it highlights the magnitude of Apple’s economic impact. Apple is making this investment in infrastructure not only comparable to the size of a country’s GDP but also as a declaration of its supremacy and its substantial capacity to invest in its corporate brand.
How Apple Influences Our Digital And Everyday Lives
In addition to revolutionizing the technology industry, Apple has become an indispensable component of millions of people’s everyday lives. The corporation affects people’s consumption of information, entertainment, and services via its goods and services such as Apple Music, Apple Watches, and iPhones. Users become a community within Apple’s meticulously designed environment as Apple services become an integral part of everyday life. Apple is now more of a cultural influence on contemporary lifestyles as a result of this degree of integration than just a tech firm.
The Impact Of Apple’s “Superpower”
To consider Apple a “superpower” is to recognize the organization’s monstrous monetary power as well as its expansive effect on numerous features of current life. Apple is a strong financial power, with a market esteem that is equivalent to that of a nation like Denmark. Apple is impacting legislative issues, culture, and the advanced scene with its gigantic client base, which is like China’s population. Similar to a nation’s diplomatic connections, the tight relationship between Apple’s CEO and world leaders highlights the company’s global significance.
Technological States Initiative
Apple As A Nation In The Technological States
Within the larger context of the Tech States series, we subject Apple to in-depth analysis. Given Apple’s enormous market capitalization, vast user base, and profound impact on many parts of modern life, the author figuratively portrays the tech giant as a “country” in recognition of its remarkable standing in the business. Apple is more than a company; it is a formidable force with social, economic, and political ramifications, and its decision underscores that.
Analyzing Apple’s Financials, International Relations, And Cultural Engagement
By modeling its operations like those of a sovereign nation, the Tech States project is able to examine Apple’s complex function. The economic landscape of Apple, including its revenue streams, market trends, and the revolutionary changes to its business model, must be examined in detail. Examines Apple’s worldwide footprint, international alliances, and contacts with other tech heavyweights as part of its “foreign policy,” among other things. In addition, by looking at how Apple’s goods and services influence social standards and habits, the study analyzes the company’s influence on cultural affairs.
Critiquing Apple’s Management, Security Operations, And Political Efforts
In order to present a comprehensive picture of Apple as a “Tech State,” thoroughly examines critical aspects of the business. Part of this process is looking at Tim Cook’s tenure as Apple CEO and how the firm has changed since Steve Jobs’ death as a result of Cook’s decisions and strategy. Furthermore, the research delves into Apple’s security operations, illuminating the steps done to uphold a culture of secrecy and safeguard confidential data. Moreover, delves into Apple’s lobbying activities, illuminating the company’s interactions with lawmakers and its impact on national and international legislative decisions.
Cupertino People’s Republic
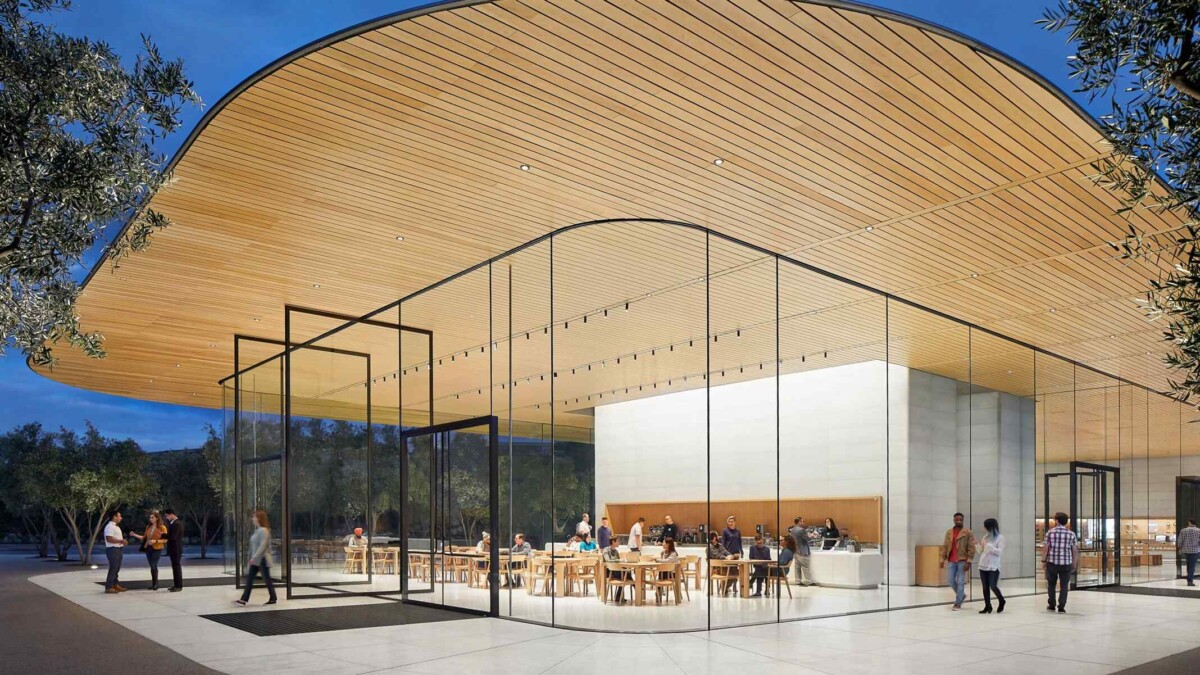

A Short Overview Of Apple Park And Its Importance
Cupertino, California’s Apple Park is home to the world-famous Apple headquarters. Designed by Foster + Partners and inspired by Apple’s departing chief design officer, Jony Ive, this architectural wonder—which cost $5 billion—features a circular design, often called “the ring.” Beyond being a place of business, the park represents Apple’s values of creativity, superior design, and employee well-being through its circular pool and artfully planted apple trees. In keeping with the company’s dedication to preserving an image of secrecy and distinction, the tremendous expense and meticulousness serve to emphasize Apple’s aspiration for an exceptional and exclusive workplace.
Cupertino And Apple’s Place In Its Interactions With The World
Apple Park has become an integral part of Cupertino’s character, in addition to its architectural importance. Economic activity, social dynamics, and property values are all profoundly affected by the company’s existence in the area. Beyond the obvious monetary effects, Apple has a profound effect on Cupertino’s social and cultural fabric as well. Cupertino, though, becomes a symbol of Apple’s principles and aspirations on a global scale, so the impact isn’t confined to just one level. The deep ties that bind a multinational tech company to the town where it is based are illustrated by the one between Apple and Cupertino.
Apple’s Methodology For Building An Original Ecosystem
Beginning from its unassuming starting points in a garage in Los Altos, California, in 1976, Apple has consistently adopted a strategy to build a really special environment. Steve Occupations, the organization’s visionary organizer, set off to give Macintosh a name and style all its own. An illustration of this strategy in real life is the 1984 Mac PC advancement. Occupations collected a band of “privateers” whose sole intention was to develop a PC with an accentuation on order and command over its equipment and programming, as well as a tastefully satisfying plan. Through the implementation of this ecosystem-building strategy, Apple aimed to cultivate brand loyalty and exclusivity by immersing users in its products in a closed, proprietary environment.
How Apple’s Control And Ecosystem-Building Strategy Influenced The Macintosh’s Evolution
One example of Apple’s control-centric strategy is the Macintosh computer. Jobs made sure that the Macintosh’s design discouraged user tinkering by making it elegant and immutable. Unauthorized access could not be achieved because the device was held together by special screws. By declining to license the OS, Apple has shown once again how serious it is about keeping its ecosystem exclusive. Users of the Macintosh were essentially trapped in an ecosystem where they could either completely embrace Apple’s services or opt out. From this vantage point, we can see how Apple’s unique closed ecosystem and its long-standing commitment to control have shaped the company’s philosophy and operations throughout the years.
The Innovations And Leadership Of Tim Cook

Cook’s Steve Jobs Comparison
Many people see parallels between Apple’s legendary co-founder Steve Jobs and Tim Cook’s leadership style. In contrast to Jobs’s charisma and vision, Cook is characterized as a leader who is more concerned with getting things done. Even while Cook has kept Apple profitable and at the top of the market since Jobs passed away, others say the business has been too preoccupied with valuation and metrics to care about truly innovative ideas.
Cook’s Emphasis On New Product Development And Market Assessment
With Tim Cook at the helm, Apple has become the most valuable tech corporation in the world, with a market price that surpasses $1 trillion. Launches of new products like the Apple Watch and incremental upgrades to the company’s flagship iPhone demonstrate Cook’s focus on sustaining and growing market valuation. While this strategy has helped Apple maintain its growth, detractors argue that the company isn’t as innovative as it was during Steve Jobs’ tenure.
Shifting Apple’s Focus To The Service Economy From Manufacturing
A sea change has taken place under Cook’s watch, as Apple has shifted its focus from making hardware to a service-based economy. The launch of Apple TV+, Apple Music, and Apple Arcade are services that demonstrate this shift. The fastest-growing area of Apple’s business is its services section, which is a result of Cook’s strategic decision to broaden the company’s revenue base beyond hardware sales.
Privacy And Security As Unique Selling Points Compared To Rivals
The increased emphasis on privacy and security is one striking feature of Tim Cook’s leadership. As an example of how Apple positions itself as a data protection leader, consider the company’s rejection to help the FBI unlock an iPhone connected to a terrorism case. Apple differentiates itself from rivals like Google and Facebook, which have been under fire for data privacy issues, by emphasizing its dedication to user privacy in its marketing and advertisements.
Dangers Connected To The New Priority On Privacy
There are hazards to this approach, even while privacy and security are key differentiators for Apple. Apple faces new obstacles as it moves into services and content creation, particularly in the streaming business where competition is fierce. Critics have also pointed out that certain third-party iPhone apps exchange data in ways that go beyond Apple’s declared principles, casting doubt on the sincerity of the company’s privacy commitment.
Insider Trading Made By Former Apple Corporate Secretary
The Five-Year-Lasting Securities Fraud By Gene Levoff Admits
Former Apple director of corporate law and corporate secretary Gene Levoff has admitted to six counts of securities fraud related to an insider trading conspiracy. Over the course of five years, Levoff was accused of stealing trade secrets pertaining to Apple’s financial performance and using them for his own benefit.
The Insider Trading Scheme
While holding important positions at Apple, Levoff engaged in insider trading from February 2011 until April 2016. Levoff had access to important, nonpublic information regarding Apple’s financial performance in his role as co-chairman of the Disclosure Committee, which was tasked with evaluating and analyzing the company’s financial materials prior to public disclosure.
Making Money Based On People’s Trust
Using proprietary information, Levoff made calculated trades in Apple shares. He profited from the company’s outstanding quarterly financial results by buying a lot of shares before the announcements were made public, and then selling it for a profit when the market responded positively. But when Apple’s performance fell short of expectations, Levoff hedged his bets by selling off a lot of stock.
Disregarding Business Regulations
Apple has quarterly blackout periods where anyone with access to nonpublic information are not allowed to trade. However, Levoff disregarded these rules. Additionally, he neglected his duty to enforce the company’s Insider Trading Policy. Without Apple’s knowledge or consent, Levoff often traded during blackout times using proprietary information.
Profit And Loss Statements
By using his insider trading strategy, Levoff was able to make roughly $227,000 on some deals and avoid losing around $377,000 on others. Insider trading undermines confidence in the stability of financial markets, according to the Federal Bureau of Investigations (FBI), which oversaw the probe.
Implications For The Law
The maximum penalty for each case of securities fraud is twenty years in prison and five million dollars in fines. On November 10, 2022, Levoff will be sentenced. Earlier, Levoff had been subject to a civil complaint brought by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for similar actions.
Recognition And Collaboration
The US Attorney, Vikas Khanna, expressed gratitude to Apple, the FBI, and the SEC for their support and collaboration during the inquiry. Even though Apple lost money in the scam, the company helped bring Levoff to justice by cooperating with authorities.
Conclusion
As we explore the baffling scene of Apple Inc, where every item sent off is a firmly arranged display and every representative is an overseer of characterized data, the meaning of holes in forming the Apple biological system turns out to be progressively obvious. Tim Cook’s period has seen a surprising change, not just as far as market valuation and plans of action but additionally in the accentuation on protection as an upper hand. The dangers and compensations of this development present difficulties for Apple’s future, with the organization now a behemoth remaining at the junction of development and an emotional meltdown.
The transaction between mystery, development, and market elements keeps on characterizing Apple’s direction in the consistently advancing tech scene. In the climax of the Apple insider trading case, Quality Levoff’s blameworthy request highlights the disloyalty of trust inside one of the world’s biggest tech organizations, underscoring the significance of defending business sector respectability against people taking advantage of special data for individual monetary benefit.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. For What Reason Is Mystery So Urgent To Apple’s Way Of Life?
Apple has developed a mysterious culture for the purpose of shielding its upper hand and guaranteeing the component of shock during item dispatches. This ethos was ingrained by Steve Occupations and has been thoroughly maintained by progressive administration, including Tim Cook.
2. How Has Tim Cook’s Authority Varied From Steve Occupations In Regards To Breaks And Data Security?
Tim Cook has strengthened Apple’s emphasis on security and privacy, multiplying down on endeavors to forestall leaks . While Steve Occupations had a similar obligation to mystery, Cook’s accentuation on security as a cutthroat differentiator is a particular part of his initiative.
3. What Dangers Does Apple Look In Changing From Equipment To A Help Based Economy?
Apple’s shift towards administrations presents difficulties, for example, expanded contest in the streaming business and possible challenges in distinctive its contributions from rivals like Netflix. The organization should explore these difficulties while keeping up with its verifiable spotlight on equipment advancement.
4. How Does Apple’s Accentuation On Protection Influence Its Relationship With Clients And Contenders?
Apple’s obligation to client security is situated as a key differentiator, upgrading relationship with clients focus on information insurance. In any case, this position has prompted conflicts with contenders and administrative examination, bringing up issues about the consistency of Apple’s security standards.
5. Which Job Do Leaks Play In Forming Public Discernments And Assumptions For Apple Items?
Leaks frequently create hypothesis and energy among Apple fans, molding public assumptions for impending items. At the same time, Apple endeavors to keep up with command over its account, utilizing leaks decisively to measure public responses while effectively fighting unapproved revelations.